三色**
首先考虑两种颜色,分别在u,v
由于路径唯一,两种颜色还是比较好求的
只要取$\left ( u,v \right )$路径中点,将树分为两半即可,每个点分别控制一半
如图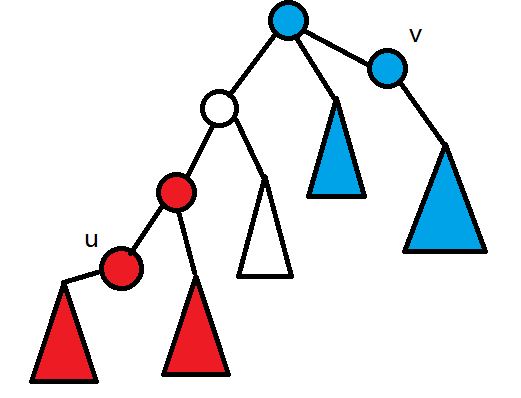
现在有三种颜色,也就是求交集
求交集可以用线段树,先把树转化为dfs 序,然后第一次区间加,第二次区间询问
不知道为什么写挂了,于是写了个分类讨论
记录一个二元组$\left ( opt,x \right )$,$x$为子树根节点,$opt=1$表示可选,0 则表示不可选
观察到两棵子树之间只有两种关系,要么不相交,要么一棵树是另一棵树的子树
判断是否相交用$LCA$即可
然后分类讨论,设两棵子树分别以$A$,$B$为根,且$A_{sz}\leq B_{sz}$
- 均可选,若两棵子树不相交则为0 ,否则为$A_{sz}$
- 均不可选,若两棵子树不相交则为$n-A_{sz}-B_{sz}$,否则为$B_{sz}$
一个可选,一个不可选
设$A_{opt}=1$,$B_{opt}=0$,这里对$sz$没有要求
- $LCA\left ( A,B \right )=A$,答案为$A_{sz}-B_{sz}$
- $LCA\left ( A,B \right )=B$,答案为0 ,但事实上并不会出现这种情况
- 否则为$A_{sz}$
1 |
|